Architecture: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
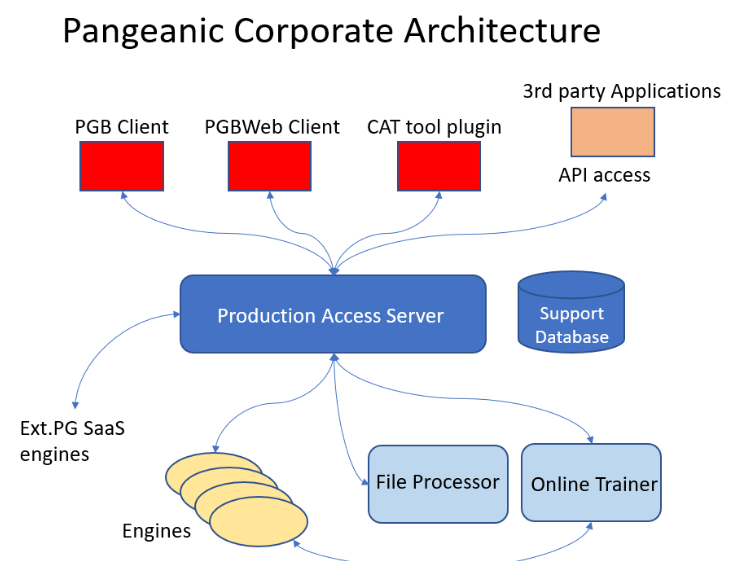
==Architecture== | |||
The diagram shows the different logical blocks. | The diagram shows the different logical blocks. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Arquitectura_wiki.png]] | [[File:Arquitectura_wiki.png]] | ||
The solution is implemented on a fully distributed architecture with different | ===The solution is implemented on a fully distributed architecture with different | ||
modules: | modules:=== | ||
* Users access the functionalities with a variety of client interfaces (described | * Users access the functionalities with a variety of client interfaces (described | ||
Revision as of 08:12, 7 February 2022
Architecture
The diagram shows the different logical blocks.
===The solution is implemented on a fully distributed architecture with different modules:===
- Users access the functionalities with a variety of client interfaces (described
later) such as the PGB, Web applications, CAT tools or programmatically with a RESTFul API for integrations.
- The Production Access Server manages user requests and orchestrates the
rest of modules. It requires a standard SQL database to store the required data to fulfil the requests.
- The engines, either local (managed by the organization on their own
premises or on their own cloud) or operated by Pangeanic with a SaaS model will perform the actual language processing.
- A file processor is in charge of dealing with converting files and documents
when this feature is installed.
- An on-line trainer module is in charge of evolving the models according to
the user preferences. This is integrated in the engine package when the on-line learning option is installed.